In today’s competitive business landscape, understanding and leveraging economies of scale can be a game-changer for companies aiming to reduce costs and enhance profitability. This article delves into the intricacies of economies of scale, exploring its benefits, types, and real-world applications, offering readers a comprehensive guide to mastering this critical economic concept.
Key Takeaways
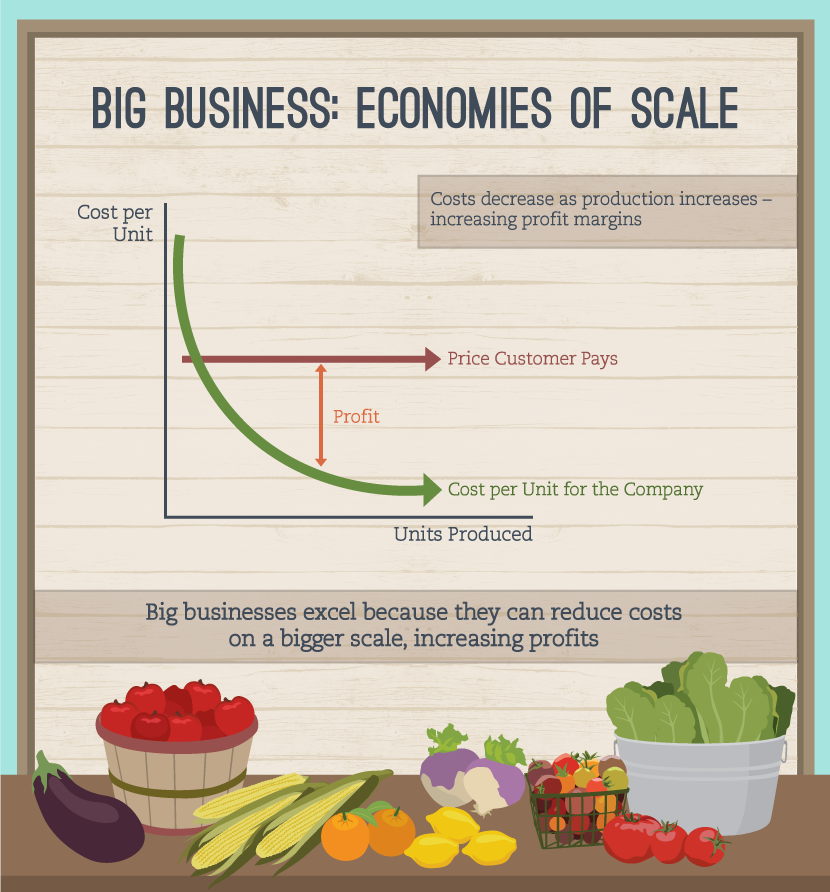
- Economies of scale refer to the cost advantages that businesses experience as their production levels increase.
- There are two main types: internal and external economies of scale.
- Understanding and implementing economies of scale can significantly enhance a company’s competitive edge.

What Are Economies of Scale?

Economies of scale occur when a company reduces its per-unit costs through increased production. These cost advantages arise because fixed costs are spread over a larger number of goods, and operational efficiencies improve with scale. As businesses grow, they can negotiate better terms with suppliers, invest in advanced technology, and optimize their workforce, all contributing to lower costs and higher profit margins.
Types of Economies of Scale
Understanding the different types of economies of scale is crucial for businesses aiming to capitalize on these advantages. The two primary types are:
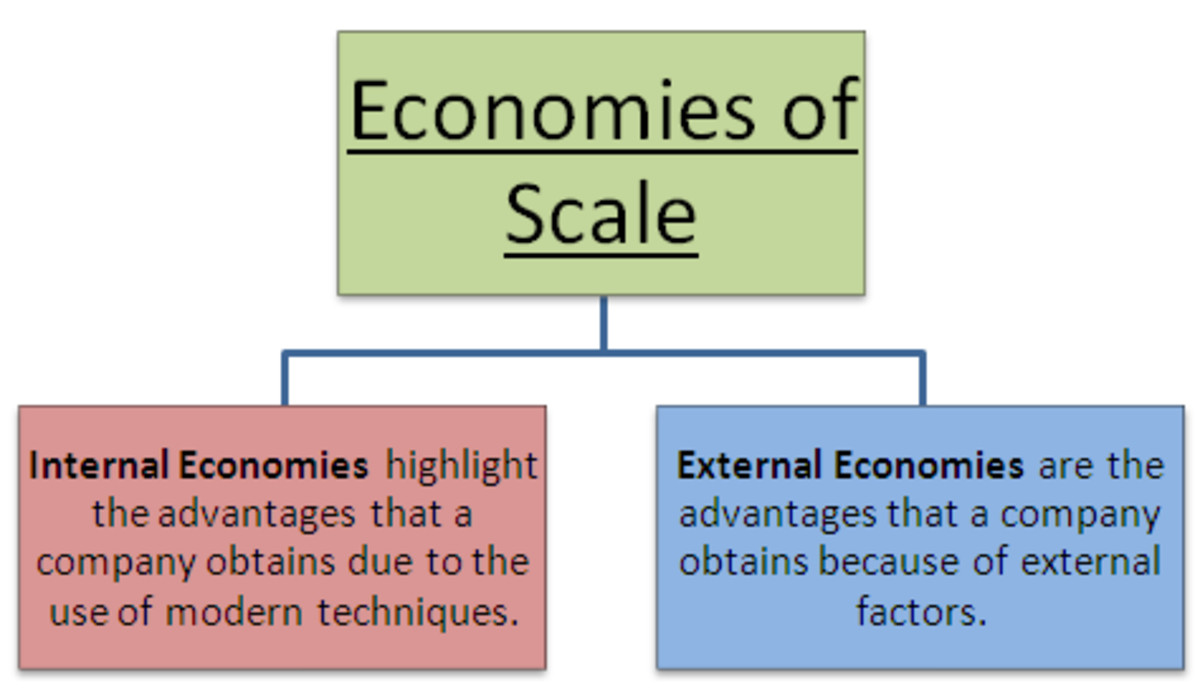
Internal Economies of Scale
These occur within a company and are a result of internal factors. They can be further categorized into:
- Technical Economies: Achieved through the use of advanced technology and efficient production techniques.
- Managerial Economies: Arise from employing specialized managers to oversee production, leading to improved efficiency.
- Financial Economies: Larger firms often enjoy lower interest rates and better credit terms due to their established reputation.
- Marketing Economies: Bulk buying and large-scale advertising reduce per-unit marketing costs.
- Network Economies: Occur when a product becomes more valuable as more people use it, common in tech industries.
External Economies of Scale
These benefits arise outside a company and are influenced by external factors such as:
- Industry Growth: As an industry expands, companies within it can benefit from shared services and infrastructure.
- Supplier Proximity: Being close to suppliers can reduce transportation costs and improve supply chain efficiency.
- Government Policies: Favorable regulations and subsidies can lower operational costs for businesses.
Benefits of Economies of Scale
The advantages of achieving economies of scale extend beyond cost savings. Here are some key benefits:
- Cost Reduction: Lower per-unit costs allow companies to offer competitive pricing, attracting more customers.
- Increased Profit Margins: Reduced costs translate to higher profit margins, enhancing financial stability.
- Market Dominance: Companies that leverage economies of scale effectively can dominate their markets, making it difficult for smaller competitors to catch up.
- Innovation and Investment: With increased profitability, companies can invest in research and development, leading to innovative products and services.
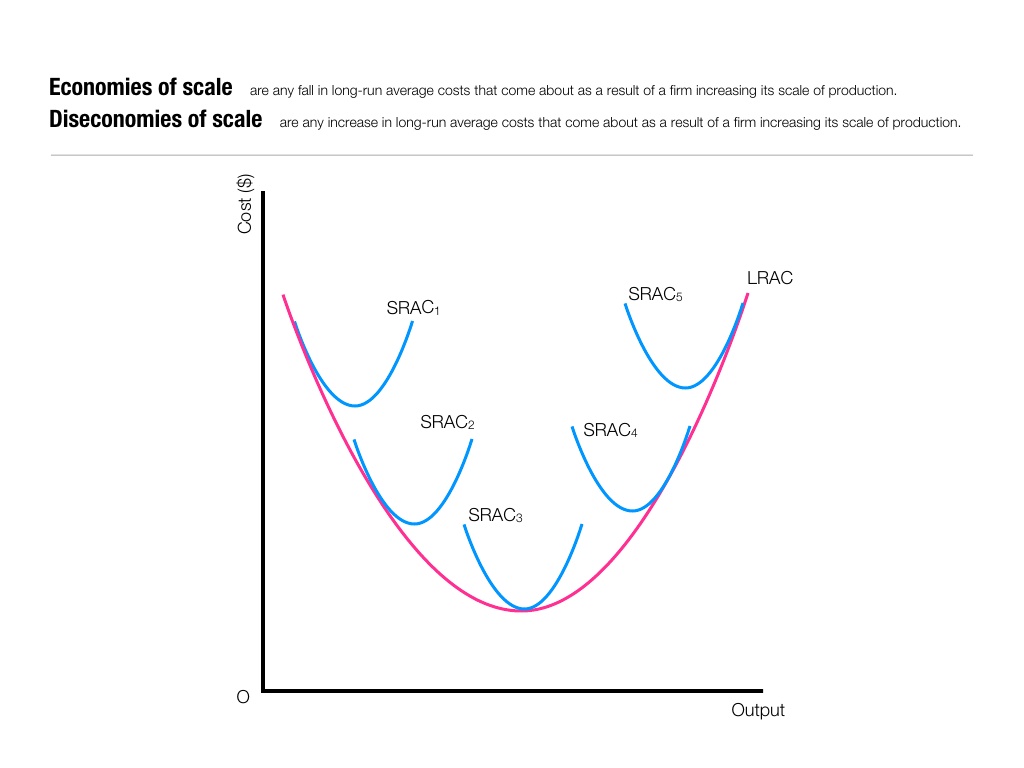
Challenges in Achieving Economies of Scale
While economies of scale offer numerous benefits, achieving them is not without challenges. Companies may face:
- Increased Complexity: As businesses grow, they may encounter operational complexities that require sophisticated management systems.
- Risk of Diseconomies of Scale: Beyond a certain point, further expansion can lead to inefficiencies, known as diseconomies of scale.
- Dependency on Suppliers: Over-reliance on a few suppliers can pose risks if there are disruptions in the supply chain.
Real-World Applications of Economies of Scale
Many industries successfully utilize economies of scale to enhance their operations and competitive positions. Notable examples include:
Automotive Industry
Car manufacturers often produce vehicles on a large scale, allowing them to reduce costs through bulk purchasing of materials and standardized production processes.
Retail Sector
Retail giants like supermarkets benefit from economies of scale by purchasing in bulk, which reduces costs and allows for competitive pricing strategies.
Technology Companies
Tech firms leverage network economies of scale, where the value of their products increases as more users adopt them, further driving sales and market penetration.
Economies of scale represent a powerful tool for businesses striving to enhance efficiency and profitability. By understanding the different types and applications of economies of scale, companies can strategically position themselves for growth and success in a competitive market. While challenges exist, the potential benefits make it a worthwhile pursuit for businesses of all sizes.
Incorporating economies of scale into business strategies requires careful planning and execution, but the rewards can be substantial, providing a foundation for long-term success and market leadership.